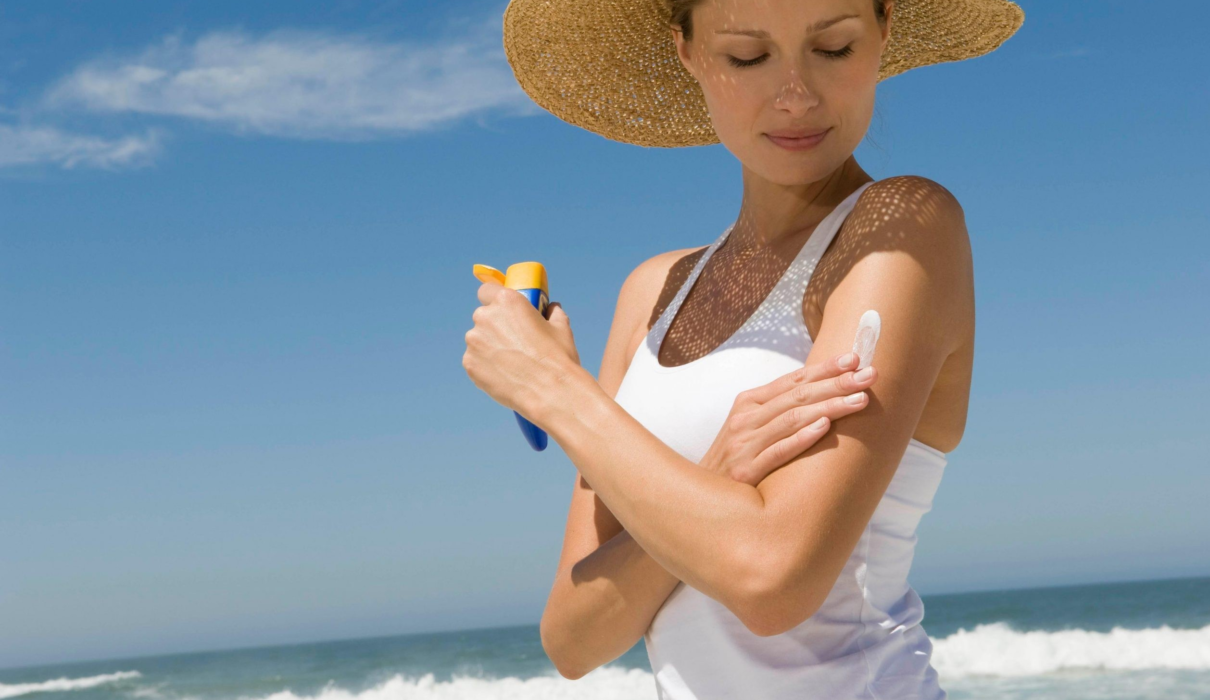
Sunscreen is something we often use to prevent sunburn, reduce the risk of developing skin cancer and help prevent early signs of skin aging. We have written for you what to consider when choosing sunscreen cream.
What is the Difference Between Solar Rays?
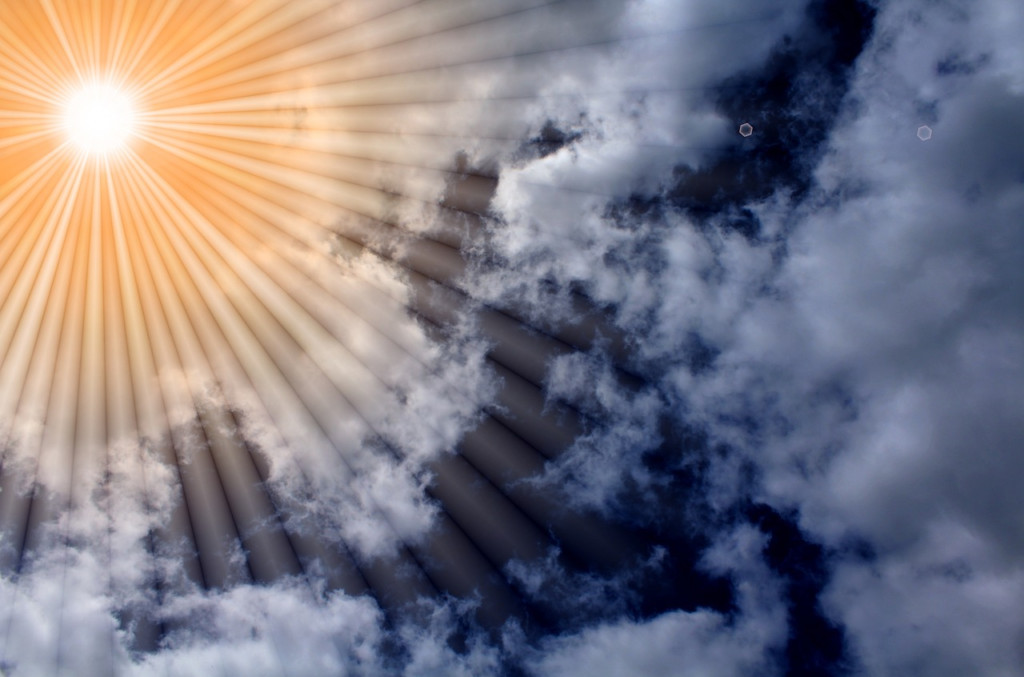

Sunlight consists of two types of harmful rays that reach the earth. These are UVA (Ultraviolet A) rays and UVB rays. Excessive exposure to both can lead to skin cancer. UVA rays (or ageing rays) can prematurely age your skin, cause wrinkles and age spots, and can pass through window glass. UVB rays (or burning rays) are the main cause of sunburn and are blocked by window glass.
UV radiation from the sun and artificial sources such as solariums and sun lamps has been declared carcinogenic.
What are Sun Protection Measures?

In addition to applying sunscreen to protect against the harmful effects of the sun, it will be useful to take the following precautions to protect your skin and detect skin cancer early:
Seek shade when appropriate, remember that the sun’s rays are strongest between 10:00 and 14:00 and try to be in the shade during these hours.
Dress for sun protection by wearing a lightweight long-sleeved shirt, trousers, a wide-brimmed hat and sunglasses if possible.
Be extra careful near water, snow and sand as they reflect the sun’s harmful rays, which can increase the chance of sunburn.
Get vitamin D safely through a healthy diet that may include vitamin supplements. Don’t seek the sun.
Avoid indoor tanning beds. Ultraviolet light from the sun and tanning beds can cause skin cancer and wrinkling. If you want to tan, you may want to use a self-tanning product, but you can continue to use sunscreen with it.
Check your skin constantly; if you notice any changes, itching or bleeding on your skin, you should consult a doctor. Skin cancer can be treated quite successfully when caught early.
Sunscreen Creams
Sunscreens are products that contain any number of UVF (ultraviolet filters) and are applied to the skin. UVF (Ultraviolet filter: Ultraviolet filter) are substances in sunscreens that have the ability to protect from the harmful effects of the sun. In order to prevent skin cancer and skin ageing, sun protective clothing and sunscreen creams should also be used. Sunscreen creams are of two types: chemical and physical sunscreen creams.
Chemical sunscreen creams work like a sponge and work by absorbing sun rays, while physical sunscreens protect the surface of your skin from sun rays like a shield.
Sunscreen creams GRASE (Generally Recognised As Safe and Effective: Generally Recognised As Safe and Effective) is very important.
SPF (Sun protection factor) is the sun protection factor. SPF is a measure of sunscreen effectiveness. SPF 30 means that when a properly applied product is used, it provides 30 times more UV exposure time than those without sunscreen.
Who Needs Sunscreen?
Everyone needs sunscreen. Using sunscreen can help prevent skin cancer by protecting you from the sun’s harmful ultraviolet rays. Anyone can get skin cancer, regardless of age, gender or race. It is estimated that one in five people have a risk of developing skin cancer during their lifetime.
What Type of Sunscreen Should I Use?
The best type of sunscreen is the one you will use over and over again. Whatever sunscreen you choose, be sure to apply it liberally to get the UV protection indicated on the product label.
The American Academy of Dermatology recommends that everyone use sunscreen that offers the following features.
Providing broad spectrum protection (protects against UVA and UVB rays),
SPF 30 or higher,
Water resistant for at least 40 minutes.
A sunscreen that offers the above helps protect your skin from sunburn, premature skin ageing and skin cancer. However, sunscreen alone cannot fully protect you.
The type of sunscreen you use is a matter of personal preference and may vary depending on the area of the body to be protected.
Available sunscreen options include lotions, creams, gels, ointments, wax sticks and sprays.
Creams are best for dry skin and the face.
Gels are good for hairy areas such as the scalp or male chest.
Sticks are good for use around the eyes.
Sprays are sometimes preferred by parents because they are easy to apply to children. Make sure you use enough of these products to completely cover all exposed skin. Do not inhale these products or apply them near heat, open flames or when smoking.
Current FDA regulations on testing and standardisation are not relevant to sunscreen sprays. The agency continues to evaluate these products to ensure safety and effectiveness.
There are also sunscreens made for specific purposes, such as for sensitive skin and infants.
Some sunscreen products are also available in combination with moisturisers and cosmetics. While these products are convenient, they need to be reapplied to get the best sun protection.
HOW TO APPLY SUN CREAM?
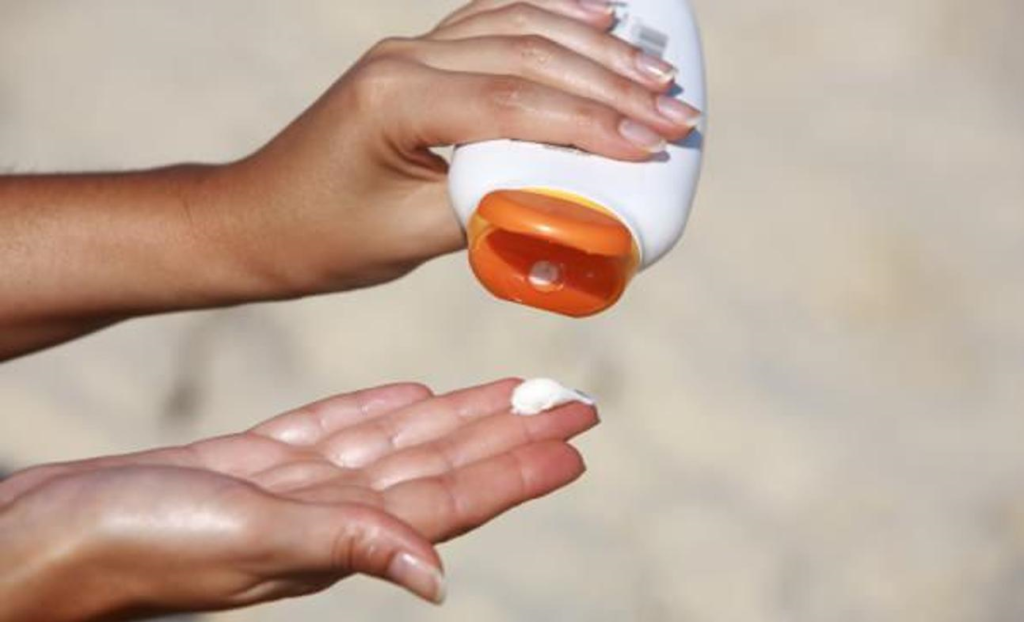

Sunscreen is safe and can protect your skin against skin cancer and premature ageing. However, it is not as effective unless it is applied correctly. Follow these tips when applying sunscreen:
Choose a sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher that is water-resistant and provides broad-spectrum coverage, which means it protects you from UVA and UVB rays.
Apply sunscreen before going outside. It takes about 15 minutes for your skin to absorb the sunscreen and protect you. If you wait until you sunbathe to apply sunscreen, your skin will be unprotected and may burn.
Apply enough sunscreen. Most adults need about 30 g or 2 tablespoons to completely cover their body. Apply sunscreen thoroughly to your skin.
Apply sunscreen to all skin that is not covered by clothing. Apply to your neck, face, ears, tops of your feet and legs. For hard-to-reach areas such as your back, ask someone to help you or use spray sunscreen. If your hair is thinning, either apply sunscreen to your scalp or wear a wide-brimmed hat. Apply a lip balm with an SPF of at least 15 to protect your lips
For protection when outdoors, reapply sunscreen every two hours or immediately after swimming or sweating. People who have been sunburned have often not used enough sunscreen, have not reapplied it after being in the sun or have used a product that has expired. Your skin is exposed to the sun’s harmful UV rays when you go outside, even on cloudy days and in winter.
So whether you are on holiday or taking a quick autumn walk around your neighbourhood, don’t forget to use sunscreen.
Few people apply enough sunscreen in the first place, and even fewer reapply it as often as recommended. Sunburns are typically the result of inadequate amounts of sunscreen, infrequent reapplication or the use of expired or denatured products (such as those stored in a car glove compartment all summer).
It is important to remind patients that UV rays are present from sunrise to sunset, even on cloudy days and in winter.
Today, UVFs are found in many cosmetic products, including facial moisturisers, eye creams, foundations, ‘beauty balms’ (BB) and ‘colour correcting’ (CC) creams, primers, lip products and even hair styling products.
In which order should I use emollients and sunscreen?
Exposure to the sun dries the skin. Try to apply your emollient about half an hour before applying sunscreen. This will prevent the sunscreen from being diluted by the emollient and ensure that the sunscreen retains its protective properties.
Babies and young children should always wear sun protective clothing with built-in SPF50. This garment is also available for adults who are sensitive to sunscreen. Sunscreen should be applied to exposed skin areas every 2 hours.
If you are using an oily emollient, be careful not to over-apply as this can cause a ‘frying’ effect in the sun.
Sunscreen creams and insect repellents
Sun cream can also be sold together with an insect repellent. It is better to buy and use these products separately. The sunscreen should be applied liberally and frequently, while the insect repellent should be used sparingly and much less frequently.
To summarise;
Provides broad spectrum protection (protects against UVA and UVB rays),
SPF 30 or higher,
Water resistant for at least 40 minutes,
It is very important that sunscreen creams are GRASE (Generally Recognised as Safe and Effective).
Adults need about 30 g or 2 tablespoons.
Apply sunscreen 15 minutes before going outside and reapply every two hours or immediately after swimming or sweating.